Page 20 - Murfreesboro, TN Comprehensive Plan: Chapter 7, Economic Development
P. 20
7.20 Chapter 7
DRAFT 12.02.15
Economic Opportunity: Another variation of TIF is where the municipality issues
public debt to provide public infrastructure and/or an
Special Financial District for Downtown upfront cash subsidy to support a project. The future
tax increments are then pledged to pay off the bonds
with the project serving as second position collateral.
As discussed in Chapter 2, Growth Capacity and For additional insurance, the municipality will typically
Infrastructure, tax increment financing (TIF) is a way require that the developer personally guarantee the
to encourage reinvestment in blighted or underutilized public bonds. In another twist, the developer may be
areas that probably won’t redevelop on their own. Put required to directly pledge his tax increment “savings”
simply, it is a way to self-finance new development toward the repayment of public (non-recourse) revenue
projects by capturing their back-end tax proceeds bonds.
to amortize front-end project costs. This happens by
setting aside new tax revenues generated within the There are many subtle variations and creative
district from the general fund for a specified period applications of the two main TIF models described
of time, usually 20+ years. The withheld amount (the here. Another model is a so-called “passive” TIF (a
“increment”) is used to pay off the district’s debts, variation of the Pay-Go model), where a district is
typically public bonds used to fund public infrastructure created in anticipation of, and/or as a stimulus for new
and/or a developer’s feasibility “gap” financing. development. However instead of using the increment
immediately to directly incent new development, the
In Tennessee, the only agencies that can issue debt, and increment is left to accumulate for a future public
administer a tax increment financing program, is either project such as a park, streetscape work or parking
a housing authority or an industrial development board. garage etc. Timing is tricky here because TIFs have a
As a result of the Uniformity in Tax Increment Financing prescribed spending or activation life that limits the
Act of 2012 reforms, State approval is now required for window for expenditures and revenue recapture. As a
a housing authority-administered TIF that lasts more general rule, passive TIFs shouldn’t be activated until
than 30 years, or an IDB-administered TIF that lasts the year that any new base revenues are expected to
more than 20 years. Additionally, local elected officials “hit” the assessment roles.
can allocate how ‘excess’ TIF revenues are allocated,
compared to previously, where a housing authority It needs to be emphasized that TIF does not mean an
could decide on its own. increase in property tax rates within the district, just
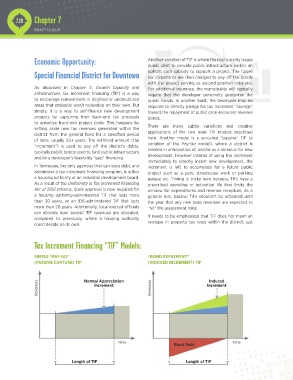
Tax Increment Financing “TIF” Models:
SIMPLE “PAY-GO” “BOND REPAYMENT”
(PASSIVE CAPTURE) TIF (INDUCED INCREMENT) TIF
Induced
Revenues Normal Appreciation Revenues Increment
Increment
Time Time
Bond Debt
Length of TIF Length of TIF